Investing in the S&P 500, one of the world’s most renowned stock market indices, has long been a popular choice for investors seeking exposure to the US equities market.
However, if you are based in Singapore, you might be wondering how to gain access to this investment and what the best approach is to invest in the S&P 500 from Singapore.
This comprehensive guide will provide you with a step-by-step process for buying the S&P 500 from Singapore. We will cover important aspects such as choosing a suitable S&P 500 ETF, offering tips for selecting an ETF broker, and more!
1. Pick an ETF tracking the S&P 500
The S&P 500 measures the performance of 500 large-cap US companies, including Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon. These companies span various sectors and represent the overall US equity market. As such, investing in the S&P 500 exposes you to a broad range of companies and can serve as a cornerstone of a diversified investment portfolio.
When it comes to investing in the S&P 500 from Singapore, it will be costly and inefficient for individual investors to attempt to invest in each of these 500 companies separately. However, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer a practical solution by providing a single investment vehicle representing the entire index’s performance. By investing in S&P 500 ETFs, Singaporean investors can effectively participate in the potential growth of the index and enjoy the benefits of diversification.
Given that the S&P 500 is a widely recognized market index, there are many ETFs listed on various exchanges.
For those who prefer to avoid international markets, the S27 SPDR®S&P 500 ETF, available on the Singapore Exchange (SGX), is your only local option for investing in an S&P 500 ETF.
The table below shows the five biggest S&P 500 ETFs available to Singaporean investors. This list was generated based on the morningstar ETF screener.
Biggest S&P 500 ETFs in Singapore
| Name | ISIN | Ticker* | Annual fee (TER) | Replication method | Use of income | Total net assets (in $B) |
| SPDR® S&P 500 ETF Trust | US78462F1030 | SPY | 0.09% | Physical | Distributing | 525+ |
| iShares Core S&P 500 ETF | US4642872000 | IVV | 0.03% | Physical | Distributing | 460+ |
| Vanguard S&P 500 ETF | US9229083632 | VOO | 0.03% | Physical | Distributing | 420+ |
| iShares Core S&P 500 UCITS ETF | IE00B5BMR087 | CSPX | 0.07% | Physical | Accumulating | 85+ |
| Invesco S&P 500® Equal Weight ETF | US46137V3574 | RSP | 0.20% | Physical | Distributing | 55+ |
*Each fund provider offers a variety of ETFs that track the S&P 500. We have chosen one ETF from each provider to simplify the analysis in this guide. However, we encourage you to visit the morningstar ETF screener, where you can explore and evaluate all the available ETF options.
Don’t worry if you are unfamiliar with what the “Replication method” and “Use of income” mean; we’ll explain them later in this guide. Now, let’s move to the second step on how to buy the S&P 500 from Singapore.
2. Choose a good ETF broker
After selecting an ETF, the next step is to identify a reliable broker to let you invest in it. To do this, we’ll provide a brief summary of what each broker offers on their platforms.
| Broker/ETF Ticker | SPY | VOO | IVV | CSPX | RSP |
| Interactive Brokers | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Saxo Bank | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Tiger Brokers | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Moomoo | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ |
Other important factors to consider when selecting an ETF broker are the fees, minimum deposit requirements, and the range of available ETFs. Here is a summary of these factors for each broker:
| Broker | ETF Transaction Fees | Min. deposit | Number of ETFs | Regulators |
| Interactive Brokers | Varies by exchange with tiered pricing: Between $0.0005 and $0.0035 per ETF share | S$0 | 13,000+ | FINRA, SIPC, SEC, CFTC, IIROC, FCA, CBI, AFSL, SFC, SEBI, MAS, MNB |
| Saxo | Between 0.03% and 0.08% for US-based ETFs (minimum of 1/USD per order) | S$0 | 6,900+ | ASIC, FSA, FCA, SFC, MAS, FINMA, and DFSA |
| Tiger Brokers | Commission fee: 1 USD per order. Platform fee: 1/USD per order. Other fees apply. | S$1 | Undisclosed | MAS |
| Moomoo | Commission fee: 0.03% * transaction amount. Platform fee: 0.99/USD per order. |
S$0 | Undisclosed | MAS |
3. Place a “Buy Order”
Once you have chosen a suitable ETF broker and funded your account, you are ready to place a “Buy Order” for the S&P 500 ETF. For this example, we will use Interactive Brokers. However, you can follow these steps to execute your purchase with any broker:
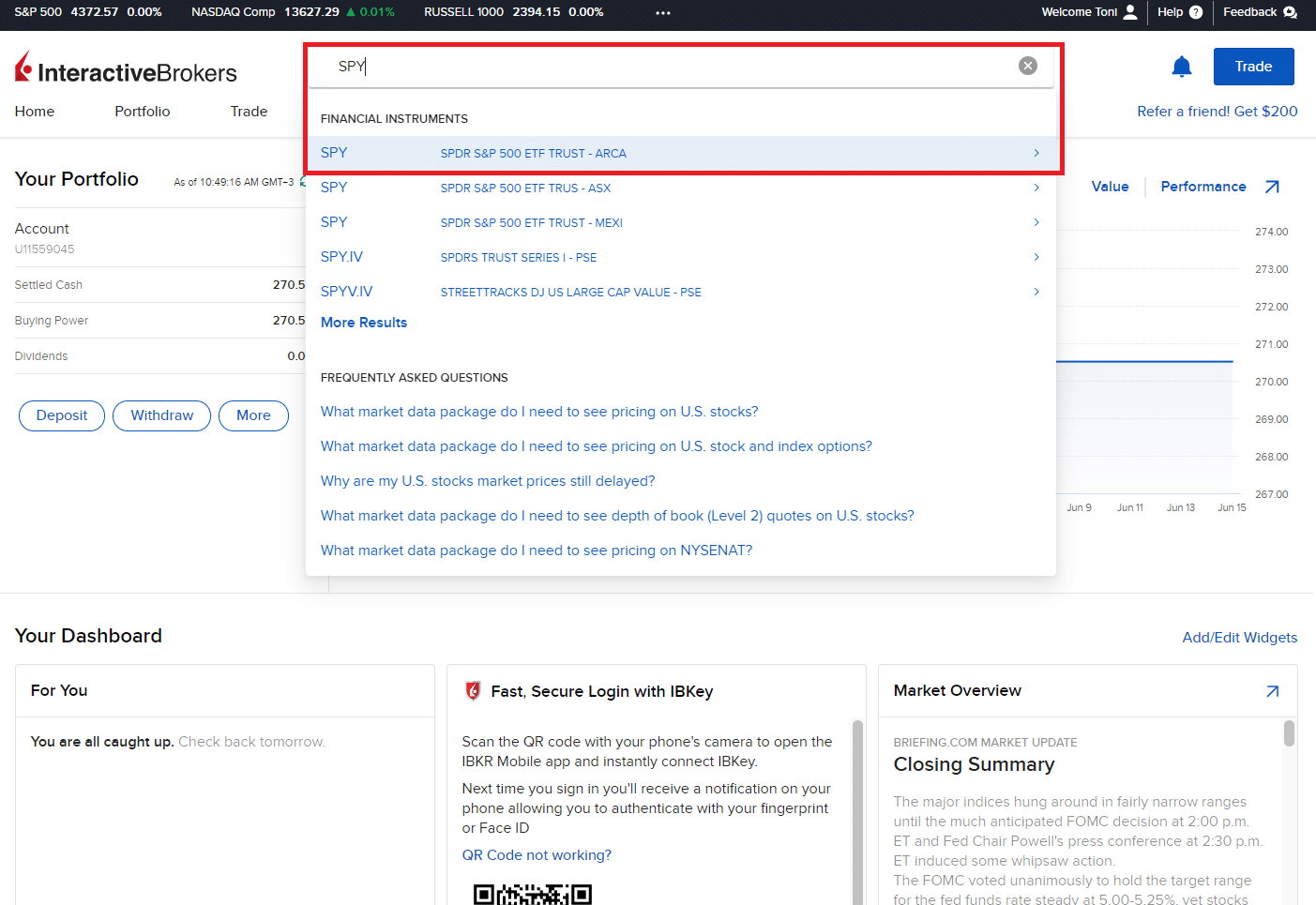
a) Search for the desired S&P 500 ETF
Use the search function or browse through the available ETFs to find the specific S&P 500 ETF you have selected. Refer to the ticker symbol to locate the ETF accurately (in our case, we searched for SPY):
You may come across instances where the broker offers multiple versions of the same ETF, denominated in different currencies such as USD or EUR. It is advisable to select the one that aligns with your account currency. For example, if your account currency is USD, choosing a USD-denominated ETF will help you avoid currency exchange fees.
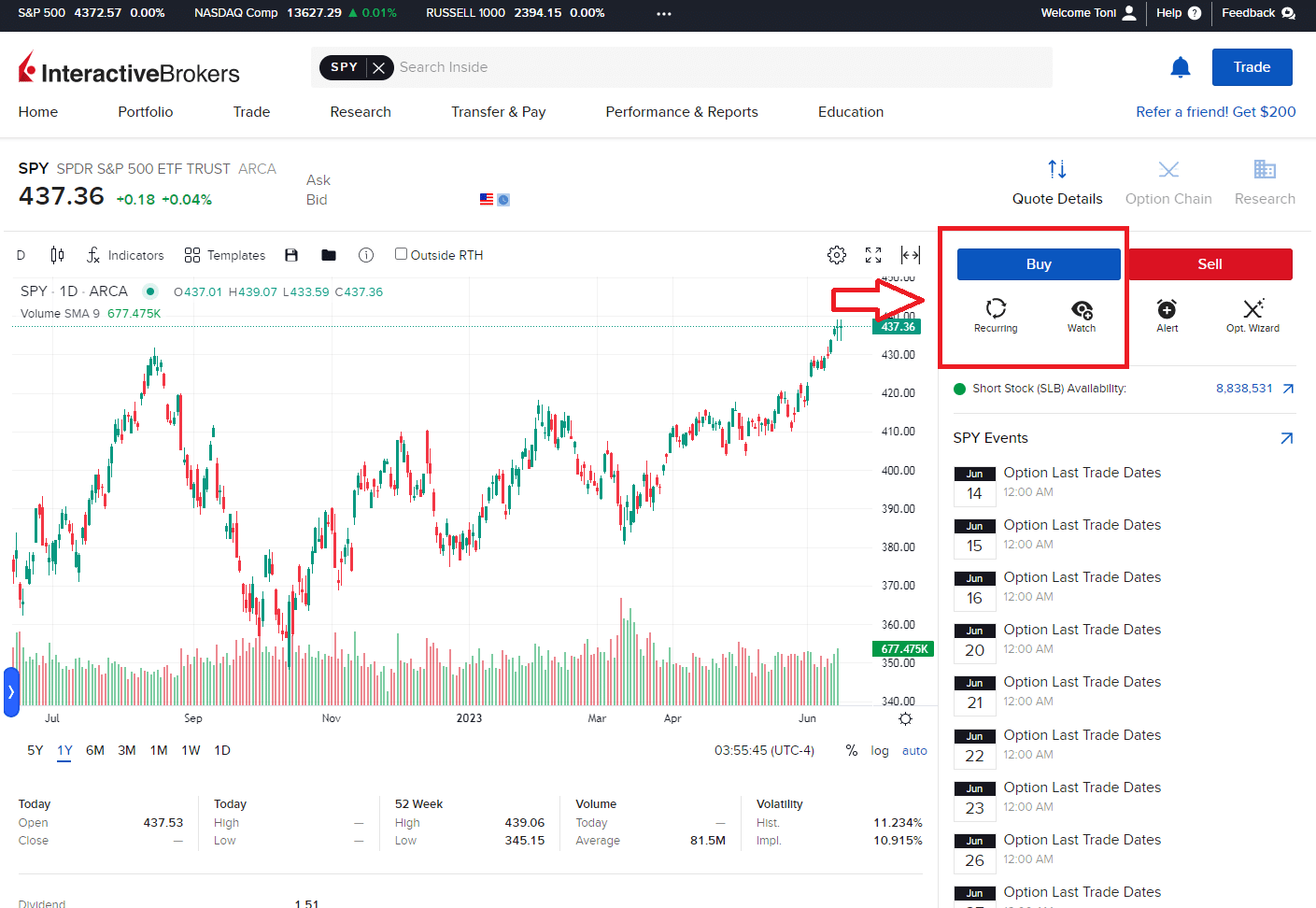
b) Click on “Buy” or “Invest”
Usually, this tab is clear once you are on the ETF page, where you will find the chart and key information about the ETF.
c) Choose the order details
Now, you must choose the appropriate order type based on your preferences and trading strategy.
- Limit Order: It is set by default on IBKR. So you can set a specific price at which you are willing to buy the ETF. The trade will only be executed if the market price reaches or falls below your specified limit price.
- Market or Trader Order: This order executes the trade at the prevailing market price and provides immediate execution.
- Amount or Units: Specify the amount of money or the number of shares you wish to invest in the S&P 500 ETF.
d) Place the order
Finally, click “Submit But Order” to submit your order. At this point, the broker will process the transaction and attempt to execute the trade at the specified parameters.
How to invest in the S&P 500 on different platforms
Below, you can find our guides made specifically for each different broker, covering how you can invest in the S&P 500. Most of them also include a Youtube video explaining step-by-step how to do it:
What to look for in any ETF?
Not all ETFs are the same, and it’s important to consider several factors before deciding. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Fees (TER)
Different asset managers charge varying fees for their ETFs. For instance, providers like BlackRock (iShares) and Vanguard charge a small annual fee, which is subtracted from the fund’s assets directly. As such, choosing an ETF with lower fees can result in higher returns on your investments. Ongoing charge (OCF) or total expense ratio (TER) are standard terms to describe this overall management fee.
Taking the SPDR® S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) as an example, you can verify its net expense ratio of 0.0945% in the fund’s factsheet:
2. Replication method
ETFs can employ two different replication methods:
- Physical replication, which involves purchasing the actual assets outlined in the index;
- Synthetic replication, where the fund manager utilizes financial derivatives to mirror index performance.
Additionally, you might encounter some ETFs that combine both approaches. Given the high liquidity of the S&P 500’s underlying companies, physical replication is often preferred due to its lower costs and reduced risks associated with derivatives.
While the SPY fact sheet doesn’t explicitly mention the replication method, the fact that the fund holds a basket of stocks implies a “Physical Replication” methodology. This is further confirmed by the FAQ section on the State Street Global Advisors website, which states the following:
3. Use of income
ETFs also differ in how they handle income generated by the underlying companies.
- Accumulating ETFs reinvest dividends received from the companies included in the index, leading to a higher ETF price. You won’t need to pay transaction fees or trading costs for dividend reinvestment, as it is done automatically.
- Distributing ETFs, on the other hand, provide regular dividend payments directly to your brokerage account, requiring you to declare the received dividends.
Ultimately, deciding between accumulating and distributing ETFs depends on your circumstances and investment strategy. Assess your long-term goals and income requirements to select the best option for your needs. For instance, if you plan to hold your investment for a relatively long period without the need for regular income, an accumulating ETF may be more suitable. However, if you aim to earn regular income from your investment, a distributing ETF would be a better choice.
When it comes to taxes in Singapore, investors are typically subjected to a 30% US dividend withholding tax on all dividends received from US-listed equities such as stocks or ETFs. This is because Singapore does not have a US tax treaty. However, the tax on capital gains can be lower based on specific criteria. As such, an accumulating ETF might be more suitable depending on your tax preferences, so it is strongly recommended to seek the guidance of a tax advisor to receive personalized advice and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
SPY is a “Distributing” ETF:
4. Size
Consider the overall fund size when selecting an ETF. Larger funds generally carry a lower risk of liquidation compared to smaller ones. In the event of liquidation, a fund sells its holdings, settles obligations, and distributes the remaining funds to investors.
The SPY has a net asset value of $527.55 million:
5. Hedging
Some ETFs employ hedging strategies using financial derivatives to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations. While this provides protection against large currency swings, it also comes at an additional cost. It’s important to note that all the ETFs mentioned earlier are denominated in USD, so it is necessary to consider the currency of the ETF when making investment decisions.
Bottom line
In conclusion, investing in the S&P 500 from Singapore is a popular option for individuals seeking exposure to the US stock market. Here’s a summary of the steps to follow:
- Pick an ETF tracking the S&P 500: Look for ETFs such as SPY and VOO, which offer competitive management fees and are listed on multiple exchanges in different currencies (this can help you circumvent potential broker-related Forex fees as you can buy in your account currency);
- Find a suitable broker: Choosing a reliable broker is crucial for investing in the S&P 500. Consider factors such as the minimum deposit and fees. In this example, we used IBKR;
- Open an account and deposit money: After deciding which trading platform to use, you must go through the account opening process and deposit money;
- Send a buy order to your broker for the picked ETF: Sending a buy order to your broker is a straightforward and intuitive process. Just fill in the required fields to execute the trade!
We hope this guide has addressed your concerns and provided valuable insights. Remember to conduct thorough research to determine the best investment strategy for your needs.
FAQs
What is the S&P 500?
The S&P 500 is a widely recognized stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 large-cap U.S. companies.
Why would someone in Singapore want to invest in the S&P 500?
Investing in the S&P 500 allows Singaporean investors to gain exposure to the US market and potentially benefit from its long-term growth.
Which brokers in Singapore offer access to S&P 500 ETFs?
Several brokers in Singapore offer access to S&P 500 ETFs, including popular platforms like Interactive Brokers, Saxo Bank, and Moomoo.
What is an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund traded on stock exchanges. It is designed to track the performance of a specific index, commodity, sector, or asset class. If you invest in an S&P 500 ETF, you will gain exposure to the performance of over 500 different companies without the need to invest in each individual company separately. This provides a convenient and efficient way to diversify your investment across a wide range of holdings within the index.
Is Robinhood available in Singapore?
Unfortunately, Robinhood is not yet available in Singapore; however, you can check our top Robinhood alternatives for some insights.
What are CFDs? Should I invest in S&P500 CFDs?
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are derivative financial instruments that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset without actually owning the asset itself. Investing in S&P 500 CFDs involves trading based on the price fluctuations of the S&P 500 index. To know more about it, you can read our article: CFDs vs Shares: Understand the Differences and check our list of the best trading platforms in Singapore.