Investing in stocks with a company account involves opening a corporate brokerage account, funding it, and then buying stocks through the broker’s platform. The process is similar to personal investing but requires adherence to business regulations. It’s crucial to define investment goals, risk tolerance, and develop an investment strategy. Always ensure your business’s financial health before investing.
The major global brokerage firm offering this service is Interactive Brokers (IBKR). It provides a robust platform for corporations, offering access to over 130 markets in 33 countries. Their advanced execution and low trading fees make it beneficial for both active and casual traders. They offer a wide range of products, impressive research tools, and high interest on cash balances. Moreover, IBKR provides flexible account structures, allowing multiple users with different functions. They also offer convenient features like Bill Pay, Electronic Money Transfers, and an IBKR Debit Mastercard. It’s a comprehensive and efficient solution for corporate trading needs.
Creating a corporate investment account with Interactive Brokers is a straightforward process that can provide numerous benefits for businesses. Here is a comprehensive step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process successfully:
How to invest through a company (step-by-step)
Step 1: Research and preparation
Before diving into the account creation process, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on Interactive Brokers‘ offerings for corporate accounts. Understand their fee structure, available investment options, and any specific requirements or restrictions that may apply.
Be aware that IBKR is not the only broker offering business brokerage accounts. We have reviewed several other brokers offering business accounts internationally, in Australia, the UK, and the US. In this article, we will focus on Interactive Brokers, since it is the broker that we have chosen to open our own business brokerage account.
Step 2: Visit the website of Interactive Brokers
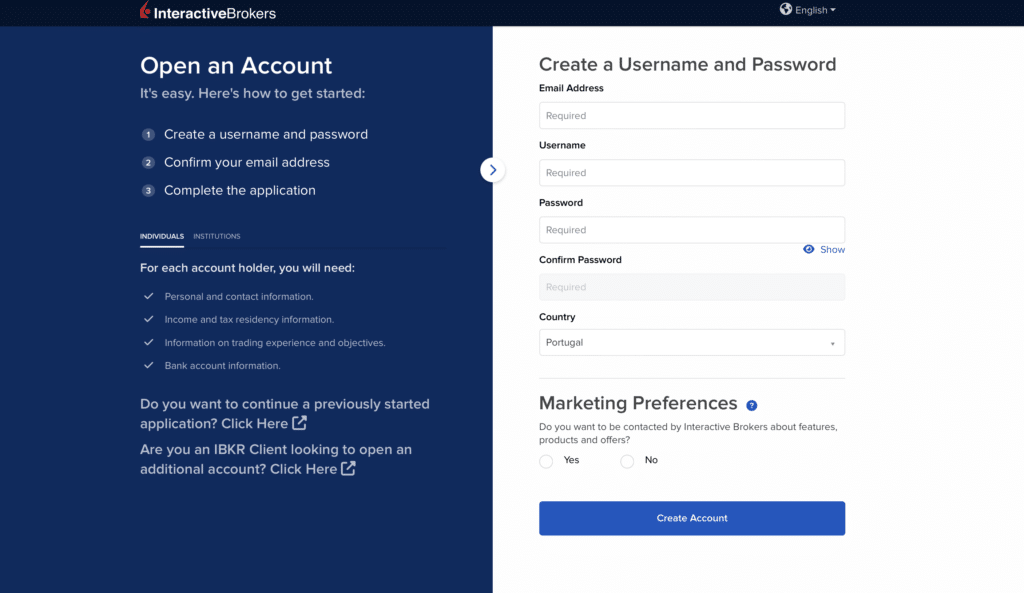
To initiate the account opening process, visit the Interactive Brokers website and look for the “Open Account” button. It’s usually prominently displayed on their homepage. Click on it to proceed.
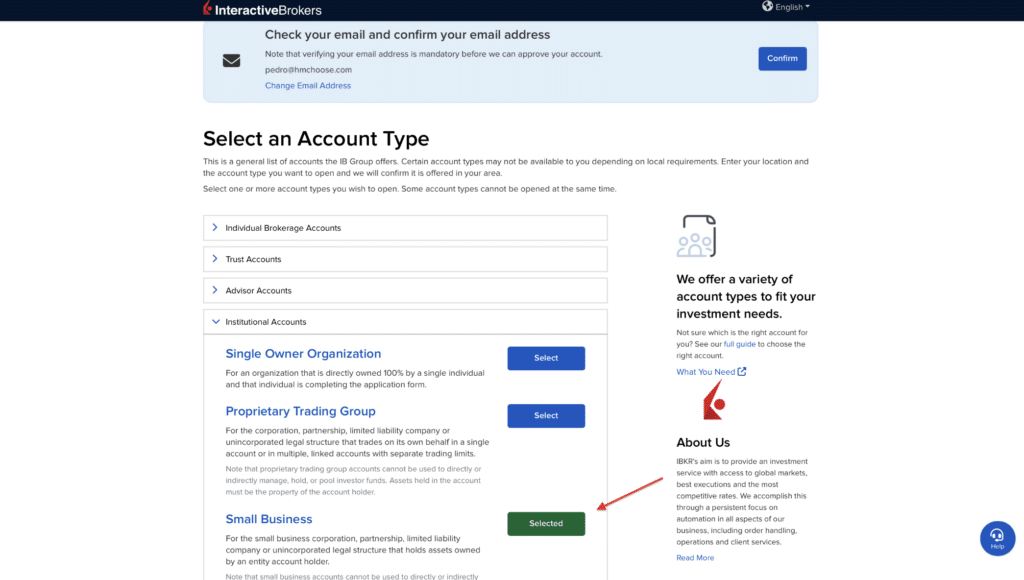
Step 3: Choose the “Small Business” option
Interactive Brokers offers different types of accounts, including individual, joint, trust, and corporate accounts. In this case, select the corporate account option when prompted. This ensures that your account aligns with your business entity.
Step 4: Complete the application
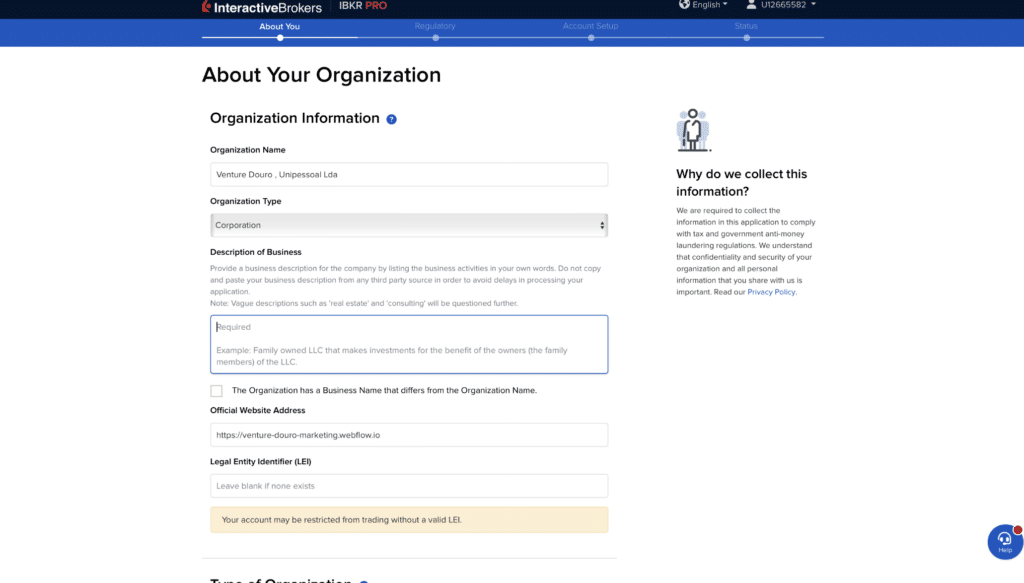
Once you have chosen the corporate account option, you will be directed to an application form. This form will require you to provide detailed information about your company, including its legal structure, industry, and financial details. Be prepared to provide the following:
- Company name, address, and contact information.
- Legal structure (e.g., corporation, partnership, limited liability company).
- Industry and nature of the business.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN) or Tax Identification Number (TIN).
- Business registration documents and certificates, such as articles of incorporation or partnership agreements.
- Financial information, including revenue, assets, and liabilities.
Ensure that all the information provided is accurate and up-to-date. Any discrepancies or errors could delay the account approval process.
Step 5: Complete regulatory information and investment objectives
As part of the application process, Interactive Brokers will require you to provide regulatory information and specify your investment objectives. This includes questions about your experience with trading and investing, previous affiliations, and any regulatory licenses you may hold.
You will also need to articulate your investment goals, such as capital appreciation, income generation, or risk management strategies. This information helps Interactive Brokers tailor their offerings to align with your specific needs.
Step 6: Review and submit the application
Once you have completed all the necessary sections of the application, take the time to review it carefully. Ensure that all the information provided is accurate and complete. Making mistakes or omitting vital details can lead to delays in the approval process.
After reviewing the application, submit it through the designated online submission process. You should receive a confirmation message or email acknowledging the receipt of your application.
Step 7: Account approval and funding
Once your application has been submitted, Interactive Brokers will review the information provided and conduct the necessary due diligence. The approval process may take some time, as the company ensures compliance with regulations and verifies the authenticity of the information provided.
If your application is approved, you will receive notification from Interactive Brokers. At this point, you can proceed to fund your account with the desired amount. Interactive Brokers offers multiple funding options, including wire transfer, check deposit, and Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers.
Step 8: Start exploring investment options
With your corporate investment account funded, you are now ready to explore the various investment options available through Interactive Brokers. The platform provides access to a wide range of investment instruments, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, options, futures, and more.
Take the time to research and understand the investment opportunities available. Consider factors such as risk tolerance, investment horizon, and diversification strategies when selecting your investments. Interactive Brokers offers a robust suite of research tools and educational resources to assist you in making informed investment decisions.
Importance of LEI (Legal Entity Identifier) as part of the account opening process
When opening a corporate account, the company needs to provide a so-called LEI. A Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a unique 20-character alphanumeric code used to identify legal entities engaged in financial transactions. It is a globally recognized identifier that helps regulators and financial institutions track and monitor financial transactions involving corporations.
The LEI system was established as a result of the 2008 financial crisis to improve transparency and mitigate risks in the global financial markets. It provides a standardized way to identify legal entities across different jurisdictions and allows for better understanding of the interconnectedness of entities involved in financial transactions.
When opening a corporate account, Interactive Brokers and other financial institutions will require a LEI as part of their Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. This requirement ensures that the corporate entity can be accurately identified and linked to its associated legal and regulatory information.
The LEI serves several important purposes:
- Enhanced regulatory oversight: By requiring a LEI, financial institutions can comply with regulatory requirements related to client identification and due diligence. The use of LEIs helps prevent money laundering, fraud, and other illicit activities by ensuring transparency and traceability of financial transactions.
- Risk management: LEIs enable financial institutions and regulators to assess and monitor risks associated with specific legal entities. The unique identifier facilitates risk analysis, monitoring of exposures, and identification of systemic risks within the financial system.
- Data standardization: The use of LEIs promotes consistency and standardization in financial reporting. It enables accurate and reliable aggregation of data across different jurisdictions, enhancing the quality and integrity of financial information.
In summary, the LEI is required when opening a corporate account to ensure compliance with regulatory obligations, enhance transparency in financial transactions, and facilitate risk management and data standardization in the global financial system.
Pros of Corporate investment accounts
Investing through a corporate account offers several advantages for businesses.
- Enhanced liability protection: By segregating business and personal assets, a corporate investment account can provide increased liability protection for business owners. This separation can help shield personal assets from potential legal claims or financial setbacks related to the business.
- Potential tax benefits and deductions: Corporate investment accounts may offer tax advantages and deductions that are not available to individual investors. Consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax benefits and deductions applicable to your business structure and investment activities.
- Access to specialized business services: Another significant benefit of a corporate account with an investment broker over a private account is the ability to access specialized business services. These may include higher transaction limits, bulk trade discounts, and dedicated support or consultancy services. These features are typically not available to individual investors, making corporate accounts more suited for larger-scale investments.
Cons of Corporate investment accounts
While corporate investment accounts offer numerous benefits, there are a few considerations to keep in mind.
- Additional paperwork and documentation: Opening and maintaining a corporate account typically involves more paperwork.
- Complexity and administrative burden: Maintaining a corporate investment account can be more complex and time-consuming compared to individual investing. Businesses may need to adhere to additional regulations, reporting requirements, and financial disclosures. This can involve extra paperwork, ongoing administrative tasks, and potentially hiring professionals such as accountants or financial advisors to ensure compliance.
- Limited liquidity: Corporate investment accounts can sometimes have restrictions on liquidity, meaning it may be more challenging to access funds quickly when needed. Some investments may have lock-up periods or withdrawal restrictions, which can limit your ability to convert investments into cash immediately. This lack of liquidity could pose challenges if the business requires immediate capital for operational needs or unexpected expenses.
- Risk of mixing business and personal finances: With a corporate investment account, there is a risk of commingling business and personal finances. If not managed carefully, this can lead to confusion, financial complications, and potential legal issues. It’s crucial to establish clear boundaries and separation between personal and corporate finances to maintain accurate accounting records and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Bottom line
Opening a corporate account for investments has several pros, including enhanced liability protection, potential tax benefits, and access to a wide range of investment options.
However, there are also cons to consider, such as increased complexity and administrative burden, limited liquidity, and the risk of commingling personal and business finances.
It’s important to carefully weigh these factors and assess how they align with your business goals and needs before deciding to open a corporate account.
Have any doubts regarding investing in stocks through your business? Feel free to contact us!