What is the difference between VUAG and VUSA? These are two ETFs that, despite having different tickers, replicate the same index, the S&P 500. The difference lies in how dividends are distributed: while VUSA distributes dividends, VUAG is accumulative.
VUSA is a distributing ETF that offers you regular dividend payments on a quarterly basis. On the other hand, VUAG is an accumulating ETF that reinvests dividends back into the fund instead of distributing them directly to you. The same provider, Vanguard, offers both ETFs.
Throughout this article, we will address all the relevant topics so you can make an informed investment decision.
VUAG vs VUSA compared in a nutshell
Our team has compiled all the information discussed throughout the article into a table, so that it can be easier for you to observe the differences and make a decision.
| ETF | VUAG | VUSA |
| Index tracked | S&P 500 | S&P 500 |
| Fund manager | Vanguard | Vanguard |
| AUM | EUR+17,000 m | EUR +35,000 m |
| Exchanges In some exchanges, the ticker for the ETFs may be different, such as in the case of VUAG on the Borsa Italiana, where it is listed as VUAA. | XMUN, XMEX, XMIL, XFRA, XLON, XETR | XPAR, XSTU, XMUN, XMEX, XMIL, XFRA, XAMS, XLON, XSWX, XETR |
| Fund currencyFund currency is the reporting currency. Still, you can trade both ETFs in currencies like the EUR, GBP, and CHF. | USD | USD |
| Dividend distribution | Accumulating | Distributing |
| Expense ratio | 0.07% | 0.07% |
Performance
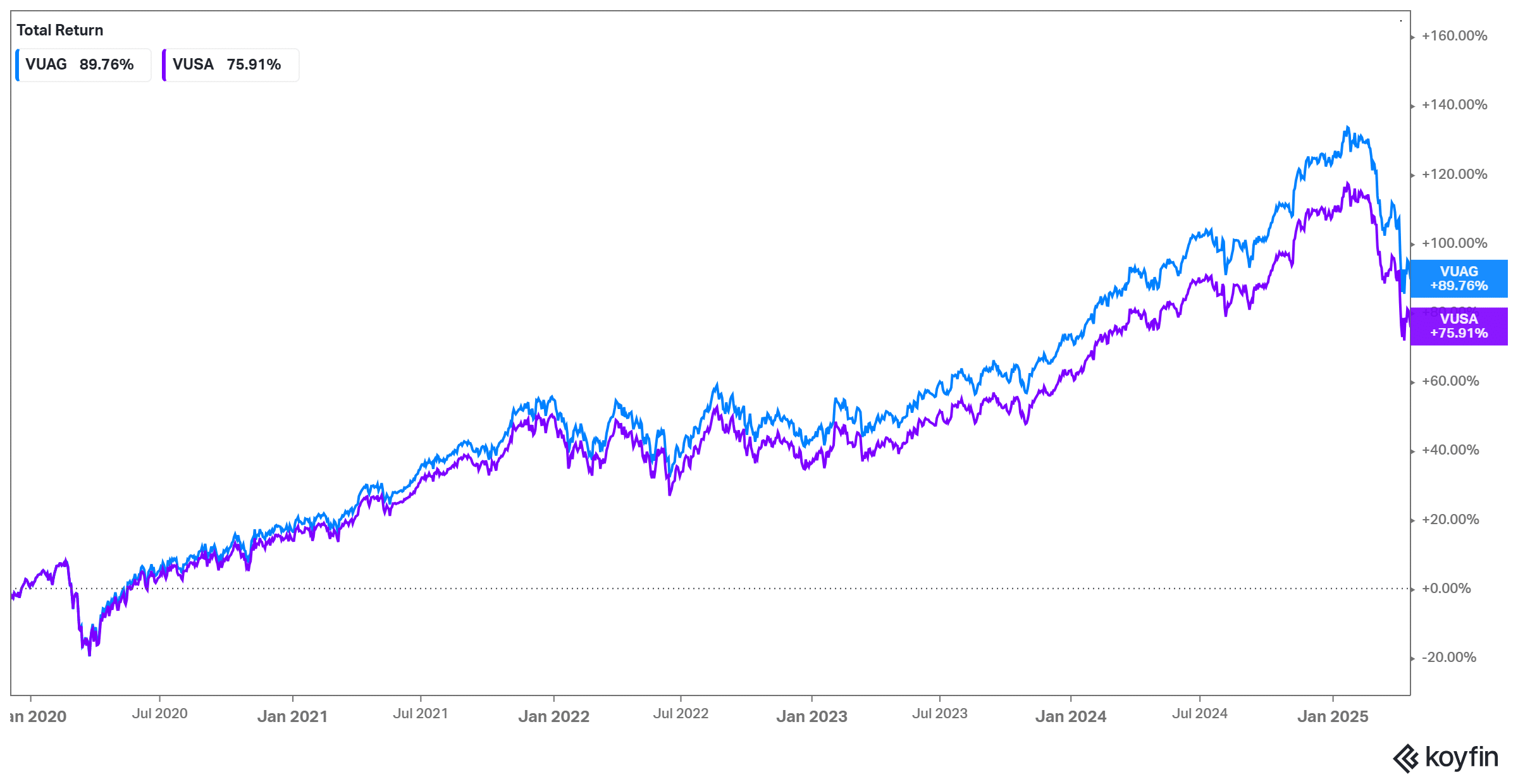
Our team has collected the historical performances of these two ETFs since 2019 (inception date of VUAG) to showcase the performance of each ETF. When comparing the performance of both ETFs, it is evident that the VUAG outperforms the VUSA.
The explanation for this phenomenon is that VUAG reinvests the dividends, whereas VUSA distributes the dividends to its shareholders. The graph only includes the price return, excluding the dividends VUSA paid.
In purple, it is possible to observe the evolution of the Vanguard S&P 500 UCITS ETF (VUSA), while in blue, it is possible to observe the trend of the Vanguard S&P 500 UCITS ETF (USD) Accumulating (VUAG).
Index tracked
Both VUAG and VUSA are ETFs replicating the S&P 500 index, which tracks the performance of 500 large-cap companies in the United States. According to the information from the fund provider, both ETFs have identical holdings, containing the same stocks in the same proportions.
Both VUAG and VUSA use physical replication as their ETF construction strategy. This means that the fund manager acquires the assets that comprise the ETF’s benchmark index, the S&P 500 Index.
AUM
VUAG was launched in May 2019, whereas VUSA was introduced in May 2012. Due to this additional seven-year head start and its listing on the US exchange, VUAG boasts significantly higher assets under management (AUM) compared to VUSA.
| ETF | VUAG | VUSA |
| AUM (millions) | EUR +17,000 m | EUR +35,000 m |
Currency
Both ETFs, VUAG and VUSA, have USD dollars (USD) as their fund currency. However, the specific tickers listed can be traded in different currencies depending on the country of the respective exchange, as is the case with the VUAG and VUSA tickers traded in GBP on the London Stock Exchange.
VUAG and VUSA are unhedged ETFs, meaning they do not use currency hedging strategies. As a result, you are exposed to currency risk (USD) when investing in these ETFs. Fluctuations in exchange rates between the ETF’s underlying currencies and your base currency can impact the overall returns of your investment.
Exchanges
As previously mentioned, the ETFs in question can be traded on different exchanges and currencies, resulting in different tickers. Therefore, our team has prepared a summary of how these ETFs may be listed on various exchanges, along with the associated currency and ticker.
| Listing | Trade Currency | VUAG | VUSA |
| Euronext Paris | EUR | – | VUSA |
| gettex | EUR | VUAA | VUSA |
| Stuttgart Stock Exchange | EUR | – | VUSA |
| Borsa Italiana | EUR | VUAA | VUSA |
| Frankfurt Stock Exchange | EUR | * | * |
| Euronext Amsterdam | EUR | – | VUSA |
| London Stock Exchange | USD | VUAA | VUSD |
| London Stock Exchange | GBP | VUAG | VUSA |
| SIX Swiss Exchange | CHF | – | VUSA |
| XETRA | EUR | VUAA | VUSA |
* You can found both ETFs in the Frankfurt Stock Exchange through their iNAV Bloomberg Code
Distribution
There is a significant distinction between the two ETFs’ distribution strategies. VUAG is an accumulating ETF that reinvests dividends back into the fund instead of distributing them directly to you. This structure may attract you if you are focused on long-term capital appreciation and the potential for higher compounding returns over time.
On the other hand, VUSA is a distributing ETF that offers you regular dividend payments on a quarterly basis. This feature can be appealing if you seek consistent income from your investments.
Tax strategy
When considering tax strategies, it’s important for you to note that VUAG and VUSA have different tax implications. As a distributing ETF, VUSA dividends are subject to taxation in the year you receive them as an investor. In contrast, with VUAG, the reinvested dividends are not immediately taxable, as they are reinvested back into the fund. Be aware that this depends on your country’s tax rules – make sure to dig deeper into your tax situation before deciding between the two ETFs.
Fund domicile
Both VUAG and VUSA are domiciled in Ireland. Investing in Irish-domiciled ETFs like VUAG and VUSA can benefit from a lower dividend withholding tax than US-domiciled ETFs.
| ETF | VUAG | VUSA |
| Dividend Withholding Tax | 15% | 15% |
If you’re not a US resident, investing in VUAG and VUSA, domiciled in Ireland, can be advantageous. Thanks to the tax treaty between Ireland and the US, VUAG and VUSA investors benefit from a reduced 15% withholding tax on dividends from US stocks.
Total expense ratio
Besides the fees you pay to your broker when trading ETF shares, there’s another cost called the total expense ratio (TER). It’s a fee charged by the fund manager to cover the expenses of running the ETF. The TER for both VUAG and VUSA is the same, at 0.07%.
| ETF | VUAG | VUSA |
| TER | 0.07% | 0.07% |
The TER is a percentage of the total amount of money in the fund and is charged daily according to its Net Asset Value (NAV) in the TER daily proportion. For instance, if it was 0.50% and you had $10,000 invested in the ETF, you would pay $50 as expenses for that year – adding all trading days (for simplicity, we consider the ETF didn’t move during this period).
Diversification
As an investor, it’s important to note that both VUAG and VUSA, as ETFs tracking the S&P 500 index, primarily focus on the U.S. stock market and its constituent companies. This means that its geographic diversification is concentrated in the United States. Consequently, VUAG and VUSA offer limited exposure to international markets or companies outside the U.S. However, most companies sell their products internationally, so you don’t only have exposure to the US. You can explore this topic in our article “Stocks: What is Your Real Country/Currency Exposure?”.
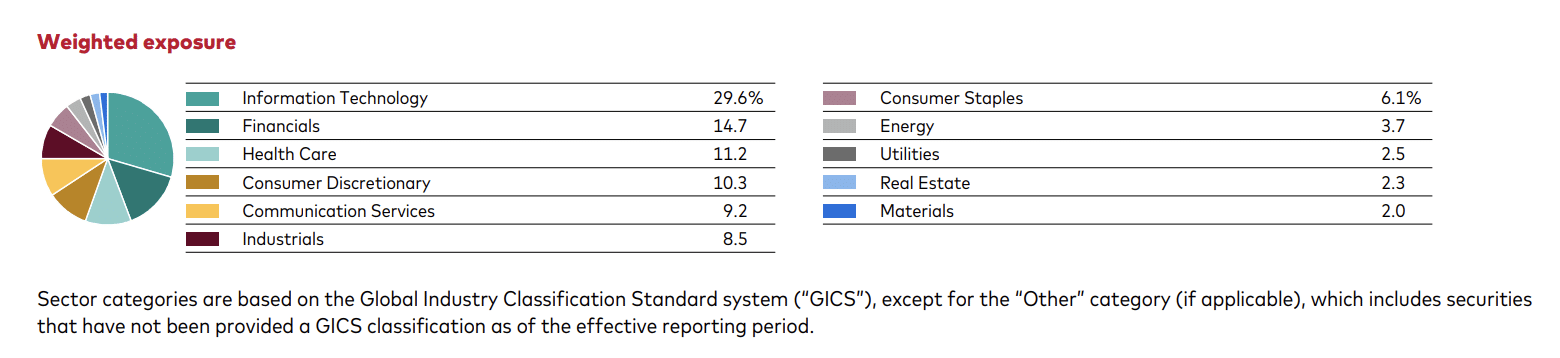
Both VUAG and VUSA ETFs diversify their holdings across various sectors of the economy, including technology, healthcare, financials, consumer discretionary, industrials, and so on. This reduces your exposure to sector-specific risks and promotes a balanced investment approach.
Cheapest brokers to invest in VUAG and VUSA
Now that we’ve gone through the differences between the two ETFs, it’s time to investigate which broker is best to invest in. We have already done that work by analysing the most important features of different ETF brokers and putting together a list of 4 ETF brokers.
Here you have the list of the 4 ETF brokers and the advantages of each one of them:
- Interactive Brokers: Best for the largest ETF offering
- Freetrade: Best for beginners
- Trading 212: Best for commission-free stock and ETF trading
- InvestEngine: Best for expert-managed portfolios
| Broker | ETF fees | Minimum Deposit | Number of ETFs | Regulators | Country |
| Interactive Brokers | Up to USD 0.0035 per stock (min: USD 0.35) for international investors | €/$/£0 | 13,000+ | FINRA, SIPC, SEC, CFTC, IIROC, FCA, CBI, AFSL, SFC, SEBI, MAS, MNB | Available worldwide (exceptions apply) |
| Freetrade | £0 | £0 | 400+ | FCA | Available in the UK and other European countries |
| Trading 212 | €/£0 | €/£0 | 600+ | FCA, CySEC, FSC | Available worldwide (exceptions apply – USA is not available) |
| InvestEngine | 0%-0.25% | £100 | 500+ | FCA | Available in the UK only. |
Do all these brokers offer both VUAG and VUSA?
| Broker | VUAG | VUSA |
| Interactive Brokers | ✔ | ✔ |
| Freetrade | ✔ | ✔ |
| Trading 212 | ✔ | ✔ |
| InvestEngine | ✔ | ✔ |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both VUSA and VUAG are popular ETFs that offer investors exposure to well-established markets, and they are both domiciled in Ireland.
VUSA is a distributing ETF, providing investors with regular dividend payments from the companies within the S&P 500 index. VUAG, on the other hand, is an accumulating ETF, which reinvests dividends into the fund, potentially offering tax advantages for investors under the Ireland-US tax treaty.
Both ETFs have the same expense ratio of 0.07%. Investors seeking regular dividend income may prefer VUSA, while those looking to benefit from potential tax advantages and automatic reinvestment of dividends might lean towards VUAG.
Ultimately, the choice between VUSA and VUAG depends on individual preferences, investment goals, and tax implications.