SPY and VOO are two popular ETFs that track the performance of the S&P 500 Index. They are very similar in performance, so their main difference is in liquidity, daily exchange volume, and fees (TER), which can lead to them being suitable for different strategies.
All in all, SPY has higher costs (TER) than VOO, and the performance of VOO has been slightly better. SPY also has more liquidity, which might be especially interesting if you’re into options trading.
In this article, you will find out more about the differences and characteristics of these ETFs so that you can choose the one that best suits your goals and strategy.
SPY vs VOO compared in a nutshell
We have assembled all the information discussed throughout the article in this table so that you can make an informed decision.
| ETF | SPY | VOO |
| Index Tracked | S&P 500 | S&P 500 |
| Fund Manager | State Street Global Advisors | Vanguard |
| AUM | +$600B | +$680B |
| Fund Currency | USD | USD |
| Dividend Distribution | Distributing | Distributing |
| Expense Ratio (TER) | 0.09% | 0.03% |
Overview
SPY: SPDR S&P 500 ETF
Launched in January 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY is the oldest ETF among all. Its goal is to provide investment results that generally correspond to the price and yield performance of the S&P 500 Index.
VOO: Vanguard S&P 500 ETF
Vanguard launched VOO in September 2010, making it a much younger fund than SPY. However, despite its relative newcomer status, VOO has quickly gained popularity among investors due to its lower expense ratio and Vanguard’s reputation for client service and investor advocacy and it is now the largest ETF tracking the S&P 500 index!
Index tracked
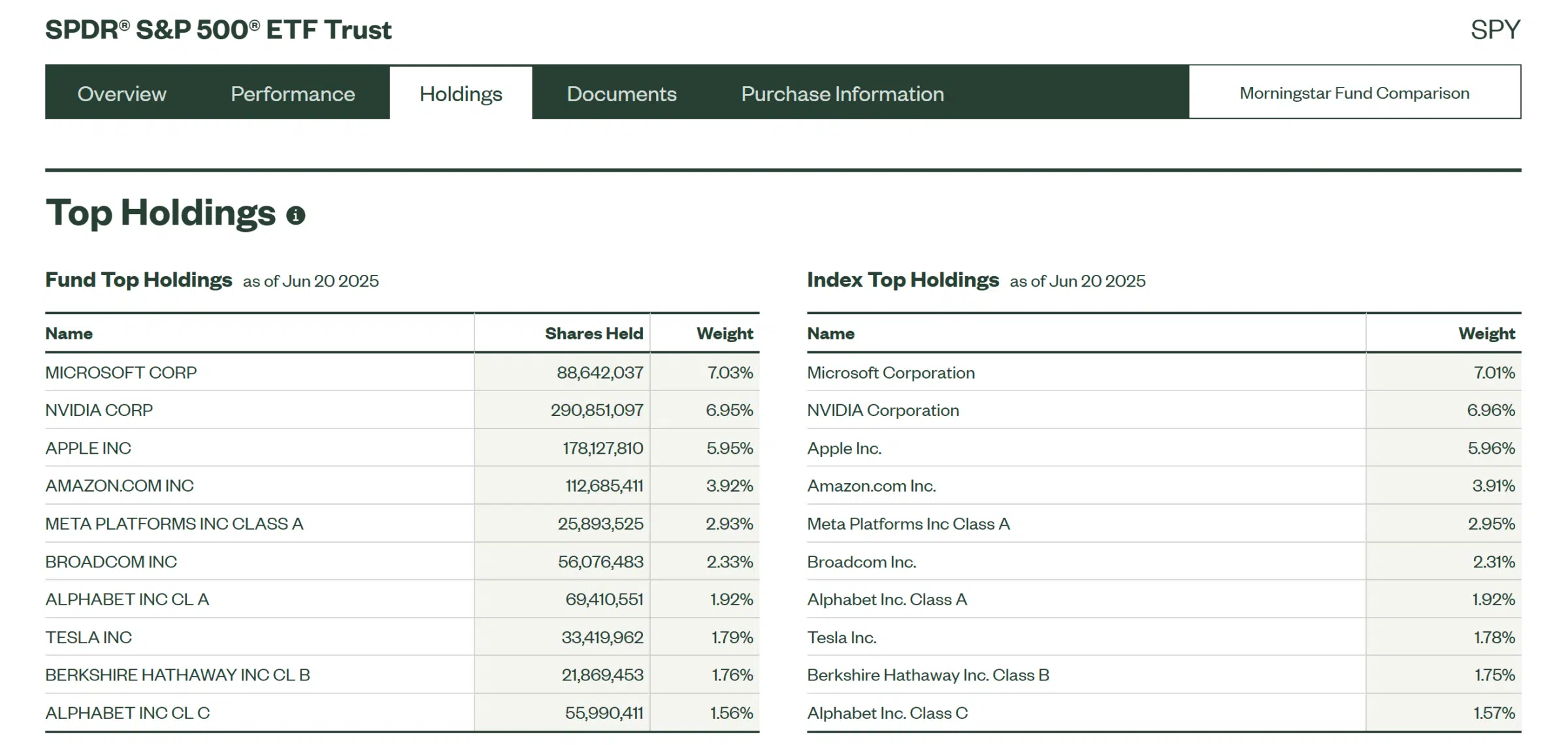
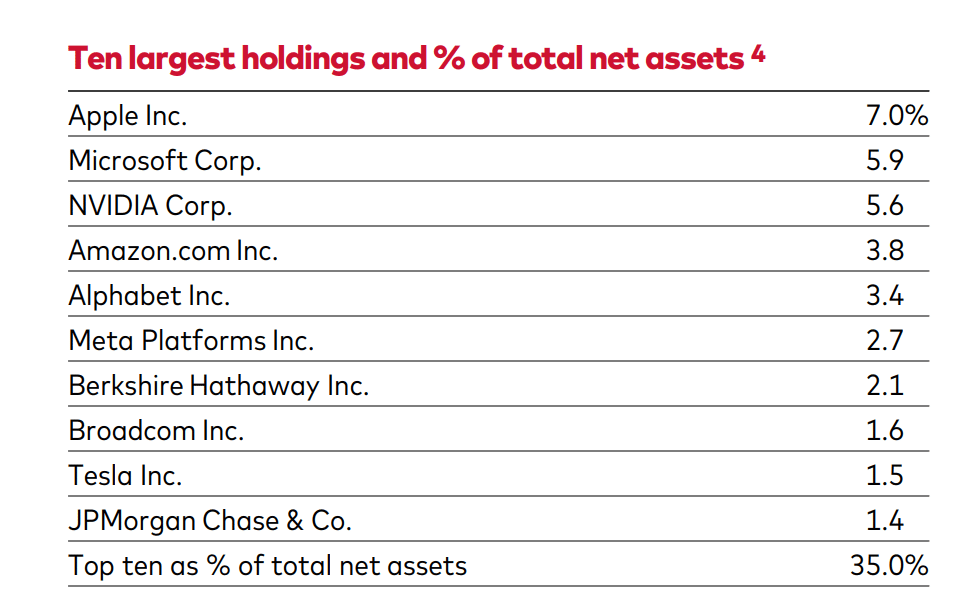
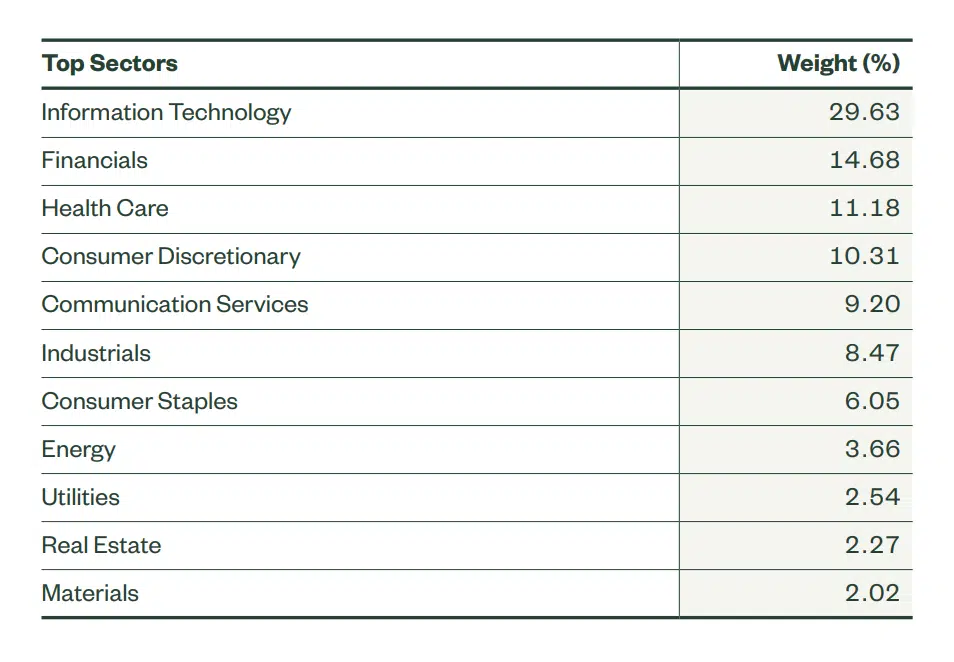
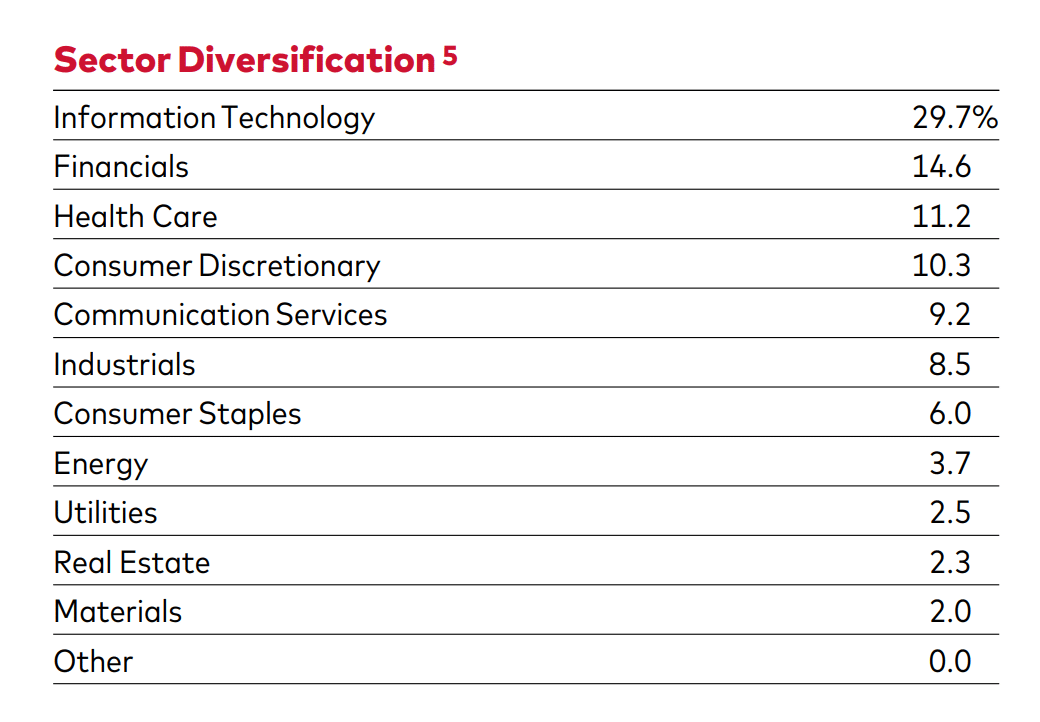
Both ETFs aim to match the performance of the S&P 500 index. So, if your interest is to invest in the US stock market, these options allow you to invest in the 500 largest companies listed on the US stock exchanges, which is why they are so popular. Despite this, there may be small differences in the composition and weight of each of these companies in the funds, as you can see below.
SPY and VOO are physical ETFs because, through full replication, they hold the underlying assets of the S&P 500 stocks at the same capitalization weight as the index.
Fund manager
Launched in 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY was the first ETF created and remains one of the most traded.
Launched in 2010, VOO is managed by Vanguard, one of the largest fund managers in the world.
Distribution
Both ETFs, SPY and VOO, are distributing ETFs which means that they offer you regular dividend payments quarterly. This distribution policy could give you the possibility to have constant income from your investment. Still, it is important to know that the dividend yield of the 2 ETFs is not very high, and if you are not from the United States, you will have to pay a dividend withholding tax, which makes it even smaller.
Total Expense Ratio (TER)
A total expense ratio reflects how much an ETF charges you for portfolio management, administration, marketing, and distribution, among other expenses. It is important to note that the expense rate directly affects the return on investment. The higher the expense rate, the lower the net return for investors.
| TER | SPY | VOO |
| TER (%) | 0.09 | 0.03 |
VOO’s expense ratio is 0.03%, among the industry’s lowest. On the other hand, SPY’s expense ratio is 0.09%, over three times that of VOO. Although this difference may seem small, over several years, it can compound and significantly impact an investor’s overall returns.
Liquidity
When looking for an ETF to invest in, you should pay attention to liquidity so that you can buy and sell at your desired price (i.e., low spreads) without waiting for your order to be fulfilled. To measure the liquidity of an ETF, it is necessary to consider some important indicators and factors. Here is some of the key information you need to know:
| Data | SPY | VOO |
| Assets under management (AUM) | +$600B | +$680B |
| Average daily volume | +$28B | +$1.1B |
| Average spread | $0.01 | $0.03 |
Source: ETF.com
These differences shown in the table indicate that if you want to buy or sell options (i.e., covered calls) on the S&P 500 index, SPY is your best option due to its superior liquidity compared to VOO. If you want to buy and hold, thinking about a long-term investment, then maybe you should look at VOO due to its lower costs (TER).
Day traders and institutional investors often favour SPY because it has significantly higher trading volume and tighter bid-ask spreads, which can lead to lower transaction costs.
Higher trading volumes generally mean better liquidity, allowing for faster execution of large-volume orders without significantly impacting the price.
Performance
Overall, SPY and VOO provide very similar returns, but if you want the closest, VOO provides the closest returns compared to the S&P 500 Index.
In the table below, you can see their average 1, 3, 5, and 10-year annual returns against the actual S&P 500 Index, accurate as of March 31, 2025. Keep in mind that the performance shown is net of expenses.
| ETF | 1-Year Return | 3-Year Return | 5-Year Return | 10-Year Return |
| SPY | 8.23% | 8.92% | 18.44% | 12.36% |
| VOO | 8.27% | 8.99% | 18.56% | 12.46% |
| S&P 500 Index | 8.25% | 9.06% | 18.59% | 12.50% |
Source: Vanguard & State Street Global Advisors
Cheapest brokers to invest in SPY and VOO
Now that we’ve gone through the differences between the two ETFs, it’s time to investigate which broker is best to invest in. We have already done that work by analysing the most important features of different ETF brokers and putting together a list of 4 ETF brokers.
Here you have the list of the 4 ETF brokers and the advantages of each one of them:
- eToro: Best for social trading and commission-free investing
- Interactive Brokers: Best for the largest ETF offering
- Public.com: Best for commission-free investing and access to an investor community
- Webull: Best for trading ETFs and access to a wide range of ETF options
Disclaimer: eToro is a multi-asset investment platform. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk. Other fees apply. For more information, visit etoro.com/trading/fees.
| Broker | ETF fees | Minimum deposit | Regulators |
| eToro | $0 (other fees apply) | $50 (varies between countries) | SEC, FINRA, FCA, CySEC, ASIC |
| Interactive Brokers | Free for US investors; Up to USD 0.0035 per stock (min: USD 0.35) for international investors | €/$/£0 | FINRA, SIPC, SEC, CFTC, IIROC, FCA, CBI, AFSL, SFC, SEBI, MAS, MNB |
| Public.com | $0 for US-listed stocks and ETFs during regular market hours; $2.99 per trade during extended hours for non-premium members | $0 | SEC, FINRA |
| Webull | $0 | $100 | SEC, FINRA, SIPC |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both SPY and VOO offer a low-cost, efficient way to invest in a diversified portfolio of U.S. equities. While SPY has the advantage regarding liquidity, VOO offers lower expense ratios and potentially better tax efficiency. The choice between SPY and VOO will ultimately depend on an individual investor’s specific needs, investment goals, and preferences.