VOO, the trading symbol of the Vanguard 500 Index Fund, is one of the easily accessible options for beginner investors to replicate the performance of the S&P 500 index.
Since its launch in 2010, VOO has grown its assets to almost $900 billion, helping spread its fixed expenses over a wide asset base. As a result, VOO remains a low-cost option for investors of all sizes, from individuals just starting to invest to institutions with decades of experience in the markets!
In this article, we’ll share tips for choosing a stock broker to buy the VOO exchange-traded fund (ETF), provide a step-by-step guide to help you make your first purchase, highlight data provided by the ETF sponsor Vanguard, delve deeper into the reporting structure of VOO, and more!
How to buy the VOO ETF (Step-by-step guide)
1. Choose a good stock broker
Since VOO is among the largest ETFs tracking the S&P 500 index, you can choose from many brokers to help you purchase. That said, consider the terms offered by each broker and ensure the broker you pick works with residents of your country. Below, we highlight four brokers which offer VOO:
| Broker | Stock commission, US | Minimum Deposit | Available countries |
| eToro | $1 | $50 (varies for different countries) | Worldwide – exceptions apply. |
| Interactive Brokers | Free for US investors; Up to $0.0035 per share with a minimum of $0.35 for international investors | $0 | Worldwide – exceptions apply. |
| Trading 212 | €/£0 | €/£10 | Worldwide. Not available in the US and other countries. |
| Saxo Bank | Up to 0.08% (min. $1) | $0 to $10,000 (varies between countries) | Worldwide. Not available in the US and other countries. |
2. Open and fund your account
Once you have weighed the pros and cons of each broker, you are all set to open an account. The process usually takes a few days as the broker verifies your identity. After the process is finalised, you must deposit money into your account.
3. Place a “Buy Order”
If you have found an online broker that suits your needs, managed to open an investment account, and made the initial deposit, you are all set to buy your ETF. All you have to do is find the ETF within your chosen broker and place a buy order. For this example, we will use eToro:
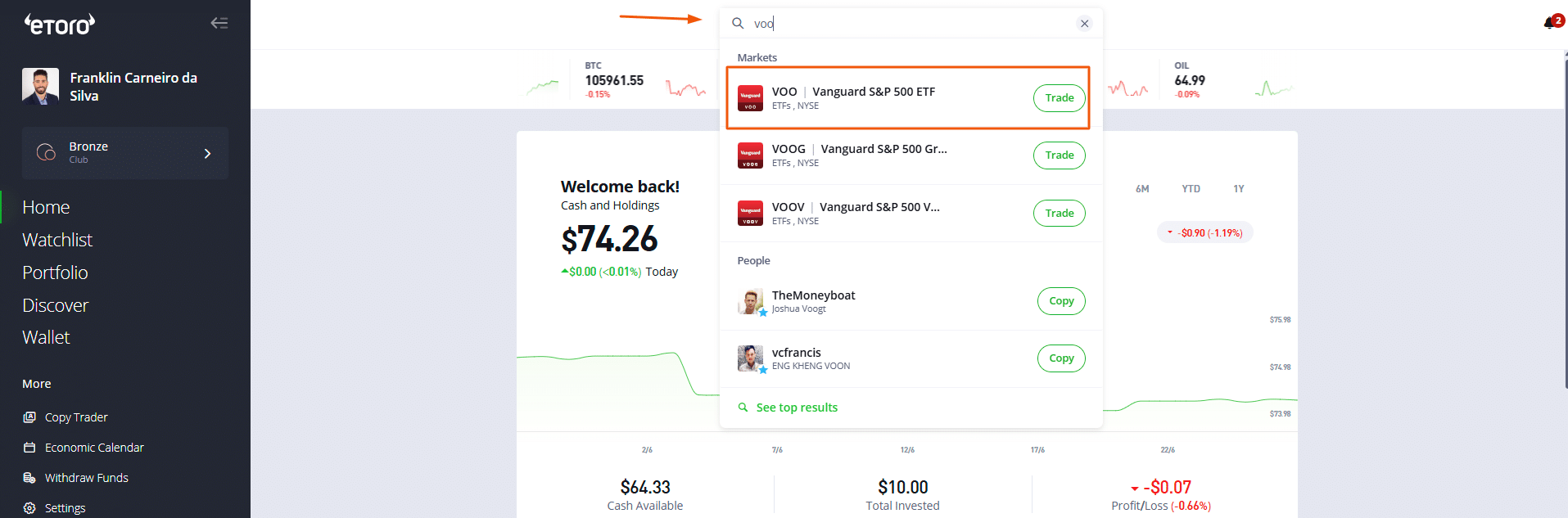
a) Search for Vanguard S&P 500 ( ticker “VOO”) and click “Trade”:
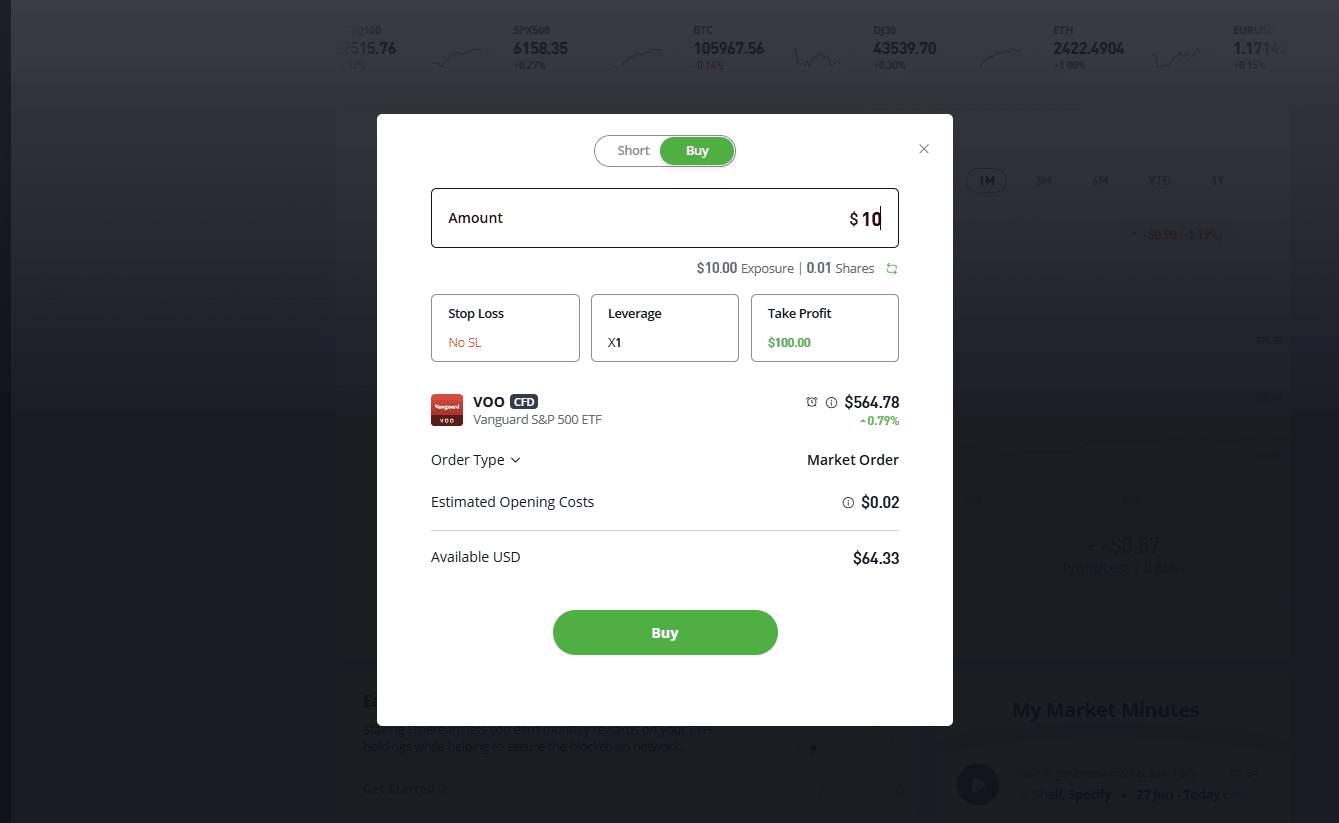
b) Choose the order details. Now, it’s time to choose how to invest:
- Amount: You choose the amount you want to invest in VOO instead of the number of shares. In this way, your investments may be fully or partially in fractional shares.
- Units: As opposed to “Amount,” here you define the number of shares you want to purchase (note: you can buy using either “Amount” or “Units,” up to you!)
- Leverage: You can choose the level of leverage. “X1” means no leverage, while “X5” means both losses are profits are multiplied by 5. That’s why you see “CFD Trade.”
- Stop Loss: Define the maximum you are willing to lose before closing your position automatically;
- Take profit: Define the profit amount that makes you close your position automatically (if reached).
Stop Loss and Take Profit are not guaranteed and trading with leverage involves high risk.
Only the “Amount” (or “Units”) and “Leverage” are mandatory fields.
d) Place the order: Finally, click “Open Trade,” a new window will show up where it says “order filled,” your exposure, and lets you share your trade with others.
VOO Overview
VOO, or the Vanguard 500 Index Fund, is an ETF that tracks one of the main US stock indices, the S&P 500 – the second-oldest US index. The S&P 500 is a capitalization-weighted index, meaning it gives a weighting to each company dependent on its market capitalisation. As a result, the largest holdings of VOO, respectively, the S&P 500’s largest components, are some of the biggest US companies:
- Nvidia at ~7%
- Microsoft at ~7%
- Apple at ~6%
Since stock indices weights and composition change constantly as prices move and new companies are added or deleted (the S&P 500 is normally rebalanced four times a year), you can find detailed information on VOO’s holdings on its dedicated website, available here.
The good thing about the VOO is that it is an excellent, low-cost (expense ratio of 0.03%) investment vehicle for beginner and entry-level investors, as all changes needed to track the performance of the S&P 500 are automatically carried out by Vanguard, who manage the ETF. You only need to allocate capital to the ETF and (hopefully) watch it grow. VOO also pays dividends quarterly.
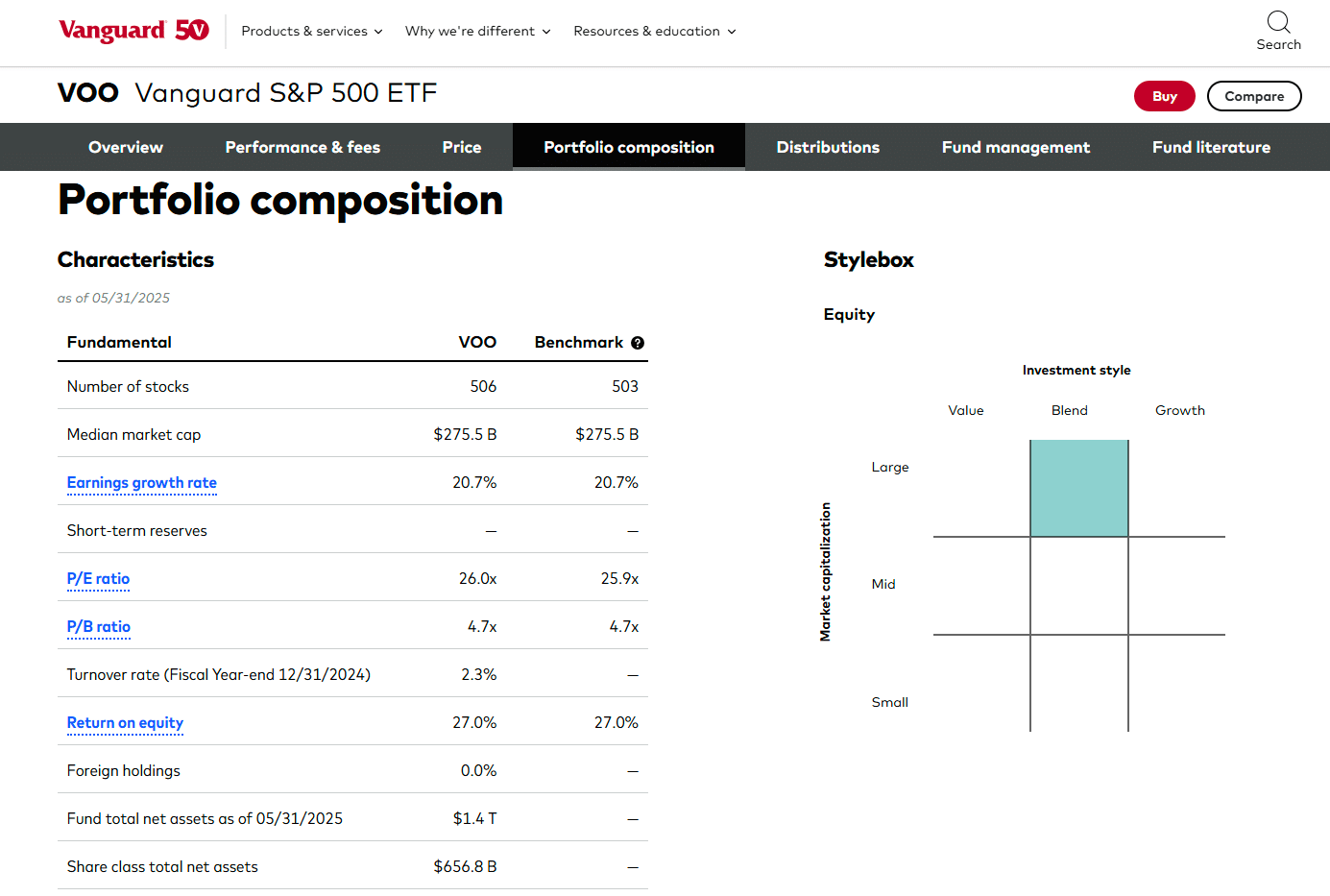
Vanguard’s website keeps track of some key statistics of VOO and its S&P 500 benchmark:
The two key ratios reported above are:
- Price-to-earnings, or P/E. A measure of the company’s profits relative to its market capitalisation.
- Price-to-book, or P/B. A measure of the company’s accounting value relative to its market capitalisation.
A good website to track where the current P/E and P/B ratios of the S&P 500 stand relative to historical norms is multpl.com.
VOO also has two distinct varieties, focused on value (companies priced attractively on accounting measures) and growth (companies expected to achieve better long-term results):
- Vanguard S&P 500 Value Index Fund (ticker VOOV) tracks 404 value companies in the S&P 500. The ETF distributes dividends, and the expense ratio stands at 0.1%.
- Vanguard S&P 500 Growth Index Fund (ticker VOOG) tracks 234 growth companies in the S&P 500. The ETF distributes dividends, and the expense ratio stands at 0.1%.
VOO’s Financials and Performance
Once you have purchased VOO ETF shares, keeping track of how VOO is doing relative to other ETFs is a good idea. Doing so will give you greater insight into whether to add to your position, hold it, or sell it to pursue better opportunities elsewhere.
Apart from Vanguard’s dedicated website (available here), there are specialised platforms to help you understand how VOO is doing from a financial perspective. One platform you can use is Koyfin – you can access ETF Holdings, Sector and Industry breakdowns, Dividend history, and more! Get a 20% discount on Koyfin.
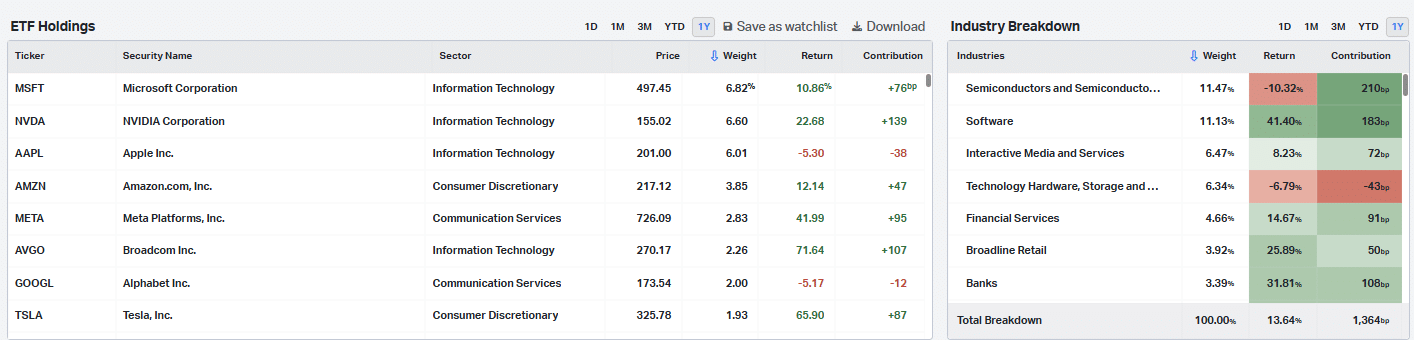
For example, Koyfin allows you to quickly handle VOO’s holdings and industry breakdown:
While such platforms cannot substitute your research 100% of the time, they can be a very useful tool in the research process, saving you time and providing new investment ideas.
Who is Vanguard?
Vanguard is the second-largest asset manager in the world, behind BlackRock. Vanguard is the asset manager that democratises index funds by offering them to the general public. You can read the company’s complete history here. Some key facts about the company are:
- Vanguard was founded in 1975.
- It currently manages +430 funds.
- It has over 50 million clients.
- It has +20,000 employees.
Hence, it is fair to say Vanguard is one of the safest options when choosing an ETF provider.
Bottom line
To sum it up, here’s what you need to do:
- Find a suitable stock broker: Make sure the broker works with residents of your country. Consider the fees and market access of the broker should you choose to diversify with other ETFs or shares as well.
- Open an account and deposit money: After deciding which trading platform to use, you must go through the account opening process and deposit money.
- Send a buy order to your broker for the ETF you like: That’s the easiest part (the process is intuitive)! After having your brokerage account funded, you just have to place a trade!
- Keep track of VOO’s financial developments: As prices move, VOO’s underlying holdings and sectors will shift over time. As a result, the relative attractiveness of VOO versus other ETFs may change. Platforms like Koyfin can help you navigate the markets!
We hope that this post addressed some of your concerns. Do your research to find the best investing strategy for you!
Happy investing!